Systematic Withdrawal Plans (SWP): A Reliable Way to Generate Regular Income
_(2).jpg)
An SWP allows investors to withdraw a predetermined amount from their mutual fund investments at regular intervals, such as monthly, quarterly or annually. The beauty of SWPs lies in their flexibility—they provide consistent income while allowing the remaining investment to continue growing.
Advantages of SWPs
1. Steady Cash Flow: SWPs are a boon for individuals who need a reliable income stream. This makes them particularly appealing to retirees or those with fixed monthly expenses.
2. Tax Efficiency: Compared to traditional options like fixed deposits, SWPs can offer tax advantages. Withdrawals from equity-oriented mutual funds, for example, may benefit from long-term capital gains tax rates, which are typically lower than income tax rates on interest income.
3. Inflation-Beating Potential: Unlike fixed-income instruments, SWPs allow for partial investment in equity funds, helping the portfolio potentially beat inflation over time.
4. Flexibility: Investors can modify withdrawal amounts, frequencies, or even discontinue the SWP if financial circumstances change.
5. Preservation of Corpus: With proper planning, an SWP ensures that only a fraction of the investment is withdrawn, leaving the rest to compound and grow.
How SWPs Work
A Systematic Withdrawal Plan (SWP) is an investment strategy that allows investors to withdraw a fixed amount of money at regular intervals from their mutual fund investments. This mechanism provides a steady stream of income while enabling the remaining investment corpus to continue compounding over time.
Here’s a breakdown of how SWPs work step-by-step:
Investment in Mutual Funds
An investor begins by investing a lump sum amount in a mutual fund, often in equity or balanced funds. These funds are designed to generate returns over time through capital appreciation and/or dividends.
Setting the Withdrawal Amount
The investor specifies a fixed withdrawal amount, which can be monthly, quarterly, half-yearly, or annual, based on their income needs. For example, in the case of Plan A, the investor chooses to withdraw Rs.20,000 monthly from a corpus of Rs.20,00,000.
Withdrawals Are Funded by Selling Units
To facilitate these withdrawals, the fund sells units from the investor’s total holdings. The number of units sold depends on:
• Withdrawal amount: How much money the investor needs.
• Net Asset Value (NAV): The price of each unit of the mutual fund at the time of withdrawal.
For instance: If the NAV is Rs.50 and the investor withdraws Rs.20,000, 400 units are redeemed (Rs.20,000 ÷ Rs.50 = 400 units).
Remaining Corpus Continues to Grow
The remaining corpus stays invested in the mutual fund and continues to grow based on the fund’s performance. For instance, in Plan A, the mutual fund grows at an annualized rate of 10%. Over time, this compounding growth helps maintain the overall value of the portfolio, even as regular withdrawals are made.
Impact of Growth and Withdrawals
The fund's growth rate determines how long the corpus can sustain the withdrawals. If the growth rate is higher than the withdrawal rate, the corpus might increase over time. Conversely, if the withdrawals are too high relative to growth, the corpus will deplete faster.
To better understand the mechanics of SWPs, consider the following example:
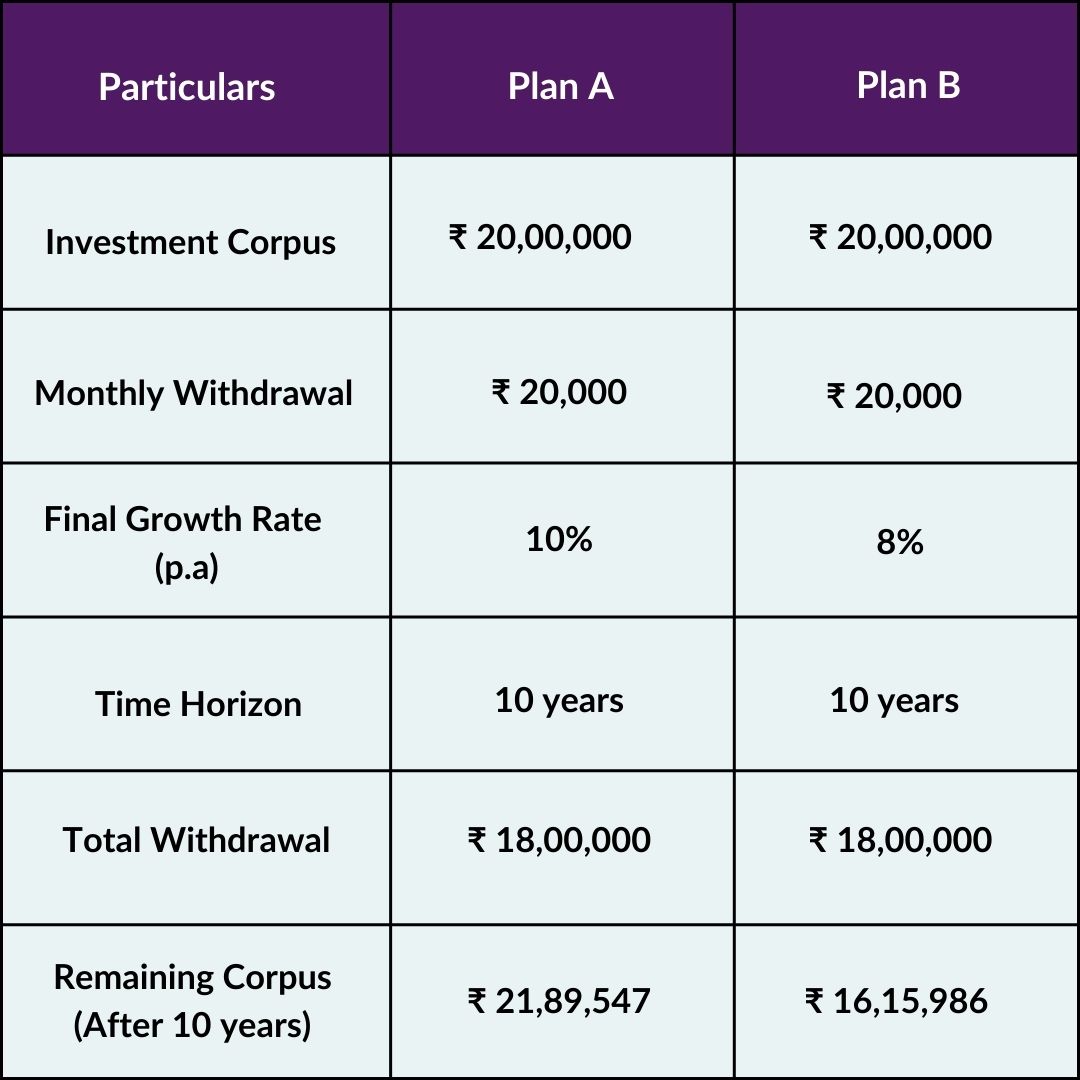
*Mutual Fund investments are subject to market risks, read all scheme-related documents carefully. Past performance is not an indicator of future returns.
• Plan A shows a healthier corpus after 10 years due to a lower withdrawal rate and a slightly higher fund growth rate.
• Plan B depletes more quickly, highlighting the importance of withdrawal discipline and fund selection.
Who Should Opt for SWPs?
1. Retirees: For retirees who no longer earn a regular salary, SWPs provide a stable income to cover living expenses.
2. Investors Seeking Tax Efficiency: Those looking for a more tax-friendly alternative to fixed deposits or rental income can benefit from SWPs.
3. Goal-Oriented Investors: Individuals needing periodic payouts for specific financial goals, such as education fees or lifestyle expenses.
Maximizing the Benefits of SWPs
1. Choose the Right Fund: Equity-oriented hybrid funds or balanced funds often strike a balance between growth and risk, making them ideal for SWPs.
2. Calculate Withdrawal Rate Prudently: Avoid high withdrawal rates to preserve the corpus over the long term.
3. Reassess Regularly: Periodic reviews of the SWP strategy ensure alignment with changing financial needs and market conditions.
Conclusion
Systematic Withdrawal Plans are a versatile financial tool, providing regular income while preserving investment potential. By integrating SWPs into a broader financial strategy, investors can achieve financial stability and peace of mind. Whether you're planning your retirement or seeking supplemental income, SWPs can be tailored to suit your needs, making them a cornerstone of goal-based investing.
By adopting SWPs as part of a disciplined investing process, you can transform your financial aspirations into actionable results—turning your Dreams into Action.
Your Investing Experts
Relevant Articles
Does Taking More Risk in Investing Really Pay Off?
Short-term comparisons often distort how investors perceive risk in the market. Understanding how risk and reward interact over time can lead to more thoughtful investing decisions.
Tax Harvesting Explained: How Investors Can Reduce Capital Gains Tax
Tax harvesting is a strategy that helps investors legally reduce the tax payable on their investments. By understanding how capital gains are taxed and when to realize gains or losses, investors can make their portfolios more tax-efficient without disrupting long-term goals.
Should You Continue Investing in ELSS and PPF in the New Tax Regime?
With Section 80C deductions removed under the new tax regime, ELSS and PPF must now stand on their investment merit. The decision is no longer about tax savings alone, it is about suitability, liquidity, and long-term goals.
.png)
.png)

